CSCI 4333 Design of Database Systems: Course Contents in Concept Maps
by K. Yue
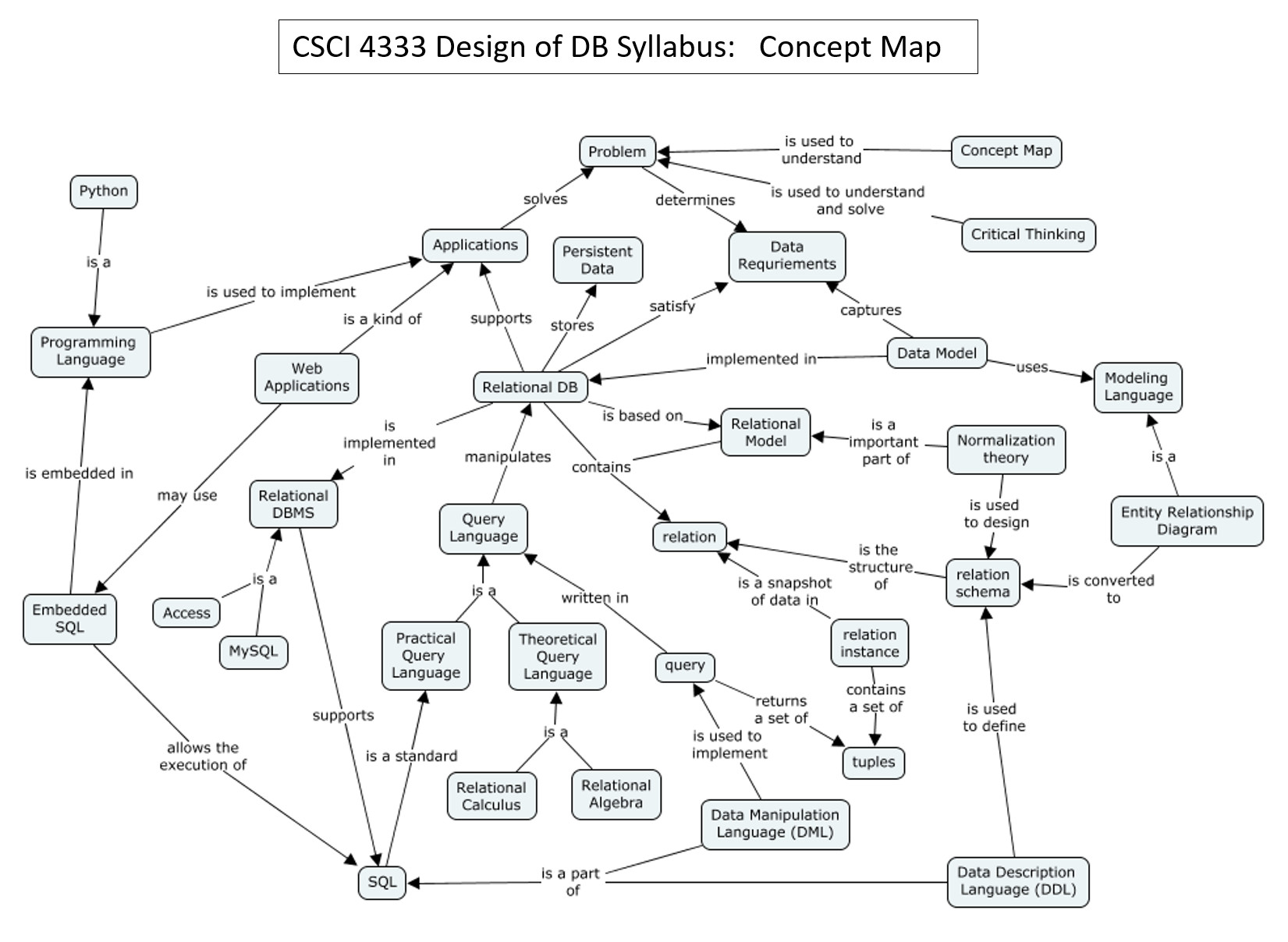
Syllabus in Concept Map
A concept map (CM) shows concepts and their relationships. There are hundreds of relevant concepts in a class. The CM below identifies the main concepts in this class and how they are related.
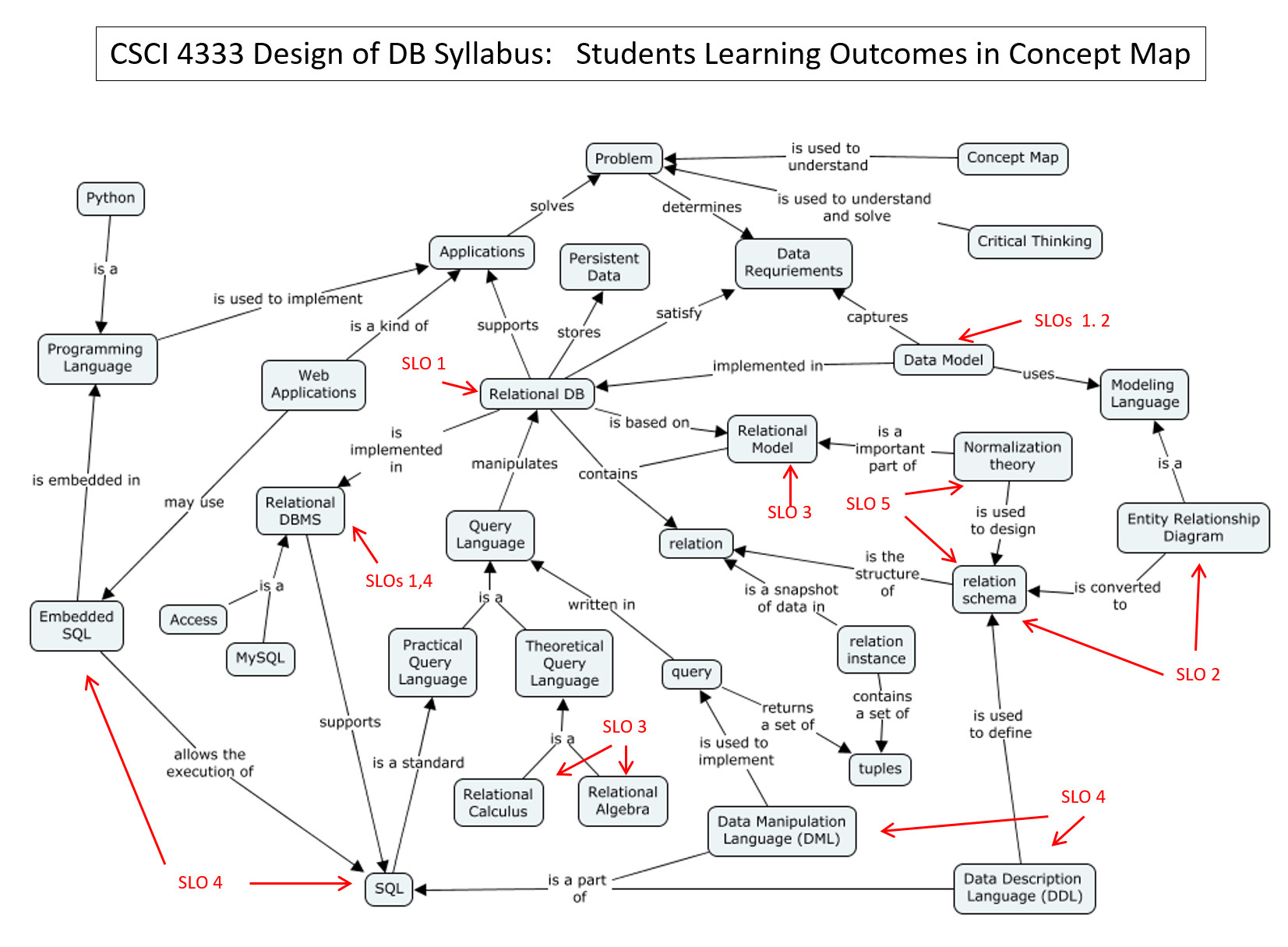
Relationships with Student Learning Objectives (SLO)
Student Learning Objectives (SLO): After completing the course, the students are expected to be able to
- Describe the stages of database design, various database architectures, and data models.
- Explain the concept of entity-relationship model, and relational model.
- Explain the theoretical background of relational database: relational algebra and relational calculus.
- Implement relational database systems using DBMS, SQL, including both data description and manipulation languages.
- Explain the importance of normalization of databases, and convert a given relational database into different normal forms.
The following CM shows how these SLOs are related.
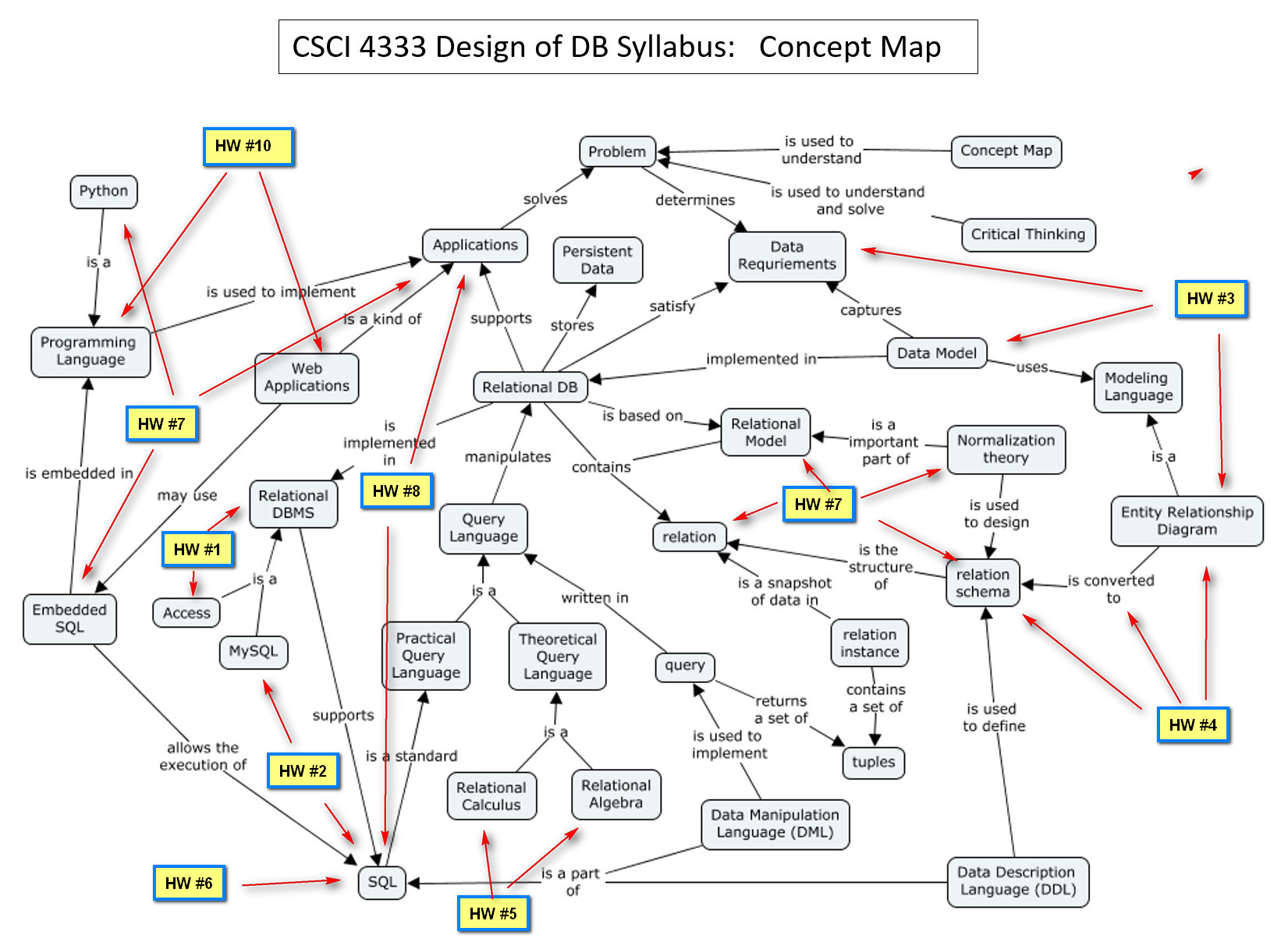
Relationships with Homework Assignments
Focuses of Homework Assignments:
- HW #1: Simple query in Microsoft Access
- HW #2: Simple queries in SQL and MySQL; Keys in the relational model
- HW #3: Constructing Entity Relationship Diagram (ERD) to capture the requirement of a database problem
- HW #4: Converting the ERD to relation schema
- HW #5: Relational Calculus, Relational Algebra and DDL in MySQL
- HW #6: Queries in SQL
- HW #7: Embedded SQL programming with Python
- HW #8: SQL Queries in Bitcoin
- HW #9: Relational DB design and normalization theory
- HW #10: Web Database Development using Python and MySQL
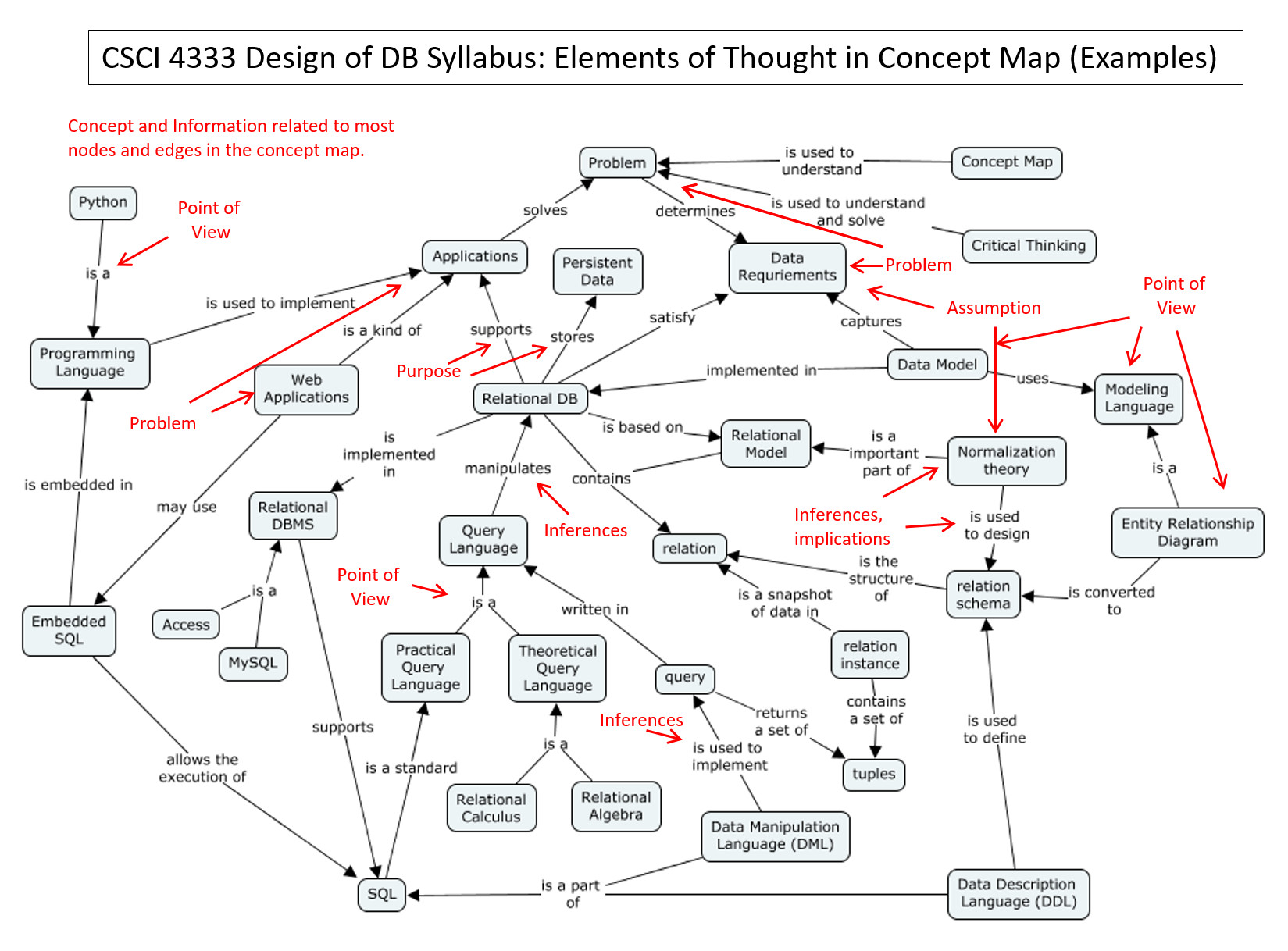
Relationships with Applied Critical Thinking (ACT)
- Foundation of Critical Thinking (FCT): model of critical thinking, https://www.criticalthinking.org/ctmodel/logic-model1.htm
- Eight Elements of Thought (EoT, or Elements of Reasoning):
- Purpose
- Question at Issue/Problem
- Information
- Interpretation and Inference/Solution
- Concepts
- Assumptions
- Implications and Consequences
- Point of View