
ITEC 3335
Database Development
Fall 2019
Applied Critical Thinking
by K. Yue
1. UHCL Quality Enhancement Plan (QEP) Motto: Applied Critical Thinking (ACT) for Lifelong Learning and Adaptability

This course has been authorized by UHCL as an Applied Critical Thinking (ACT) Course which means that in addition to learning about the specified course content, students will be engaged with some or all of the Elements of Thought and Universal Intellectual Standards of critical thinking. The objective of an ACT course is to develop the student's ability to become skilled at analysis and evaluation by applying a set of intellectual tools that may be effectively used across all disciplines (as well as to the student's personal life). Based on the Foundation for Critical Thinking model (http://www.criticalthinking.org/), critical thinking involves thinking for a purpose, asking questions, using information, applying concepts, drawing inferences and conclusions, identifying assumptions, anticipating implications and consequences, and recognizing points of view. The Universal Intellectual Standards that are applied to these Elements of Thought of critical thinking in order to develop Intellectual Traits include clarity, accuracy, precision, relevance, depth, breadth, logic, significance, and fairness.
Critical Thinking In Information Technology in General and Database Development in Particular
Information Technology is concerned with the applications of computing and communications technology to solve practical problems. For example, in Wikipedia, it is defined as "the application of computers to store, study, retrieve, transmit, and manipulate data, or information, often in the context of a business or other enterprise." The Association of Computing Machine (ACM), the professional association for computing sciences in US, defines the problem space for IT in the following diagram. IT is highly applicative in nature, with its targeted areas spanning from the organization issues and information systems level to the systems infrastructure level. Consequently, a thorough and accurate understanding and precise specification of the problem domain through modeling, with a clear understanding of all assumptions and relevant information is a prerequisite for effectively using IT to construct an effective solution. In fact, all elements of thought of critical thinking are essential in every step of the elaboration and modeling of the problem, and the design, implementation, and maintenance of an IT solution.
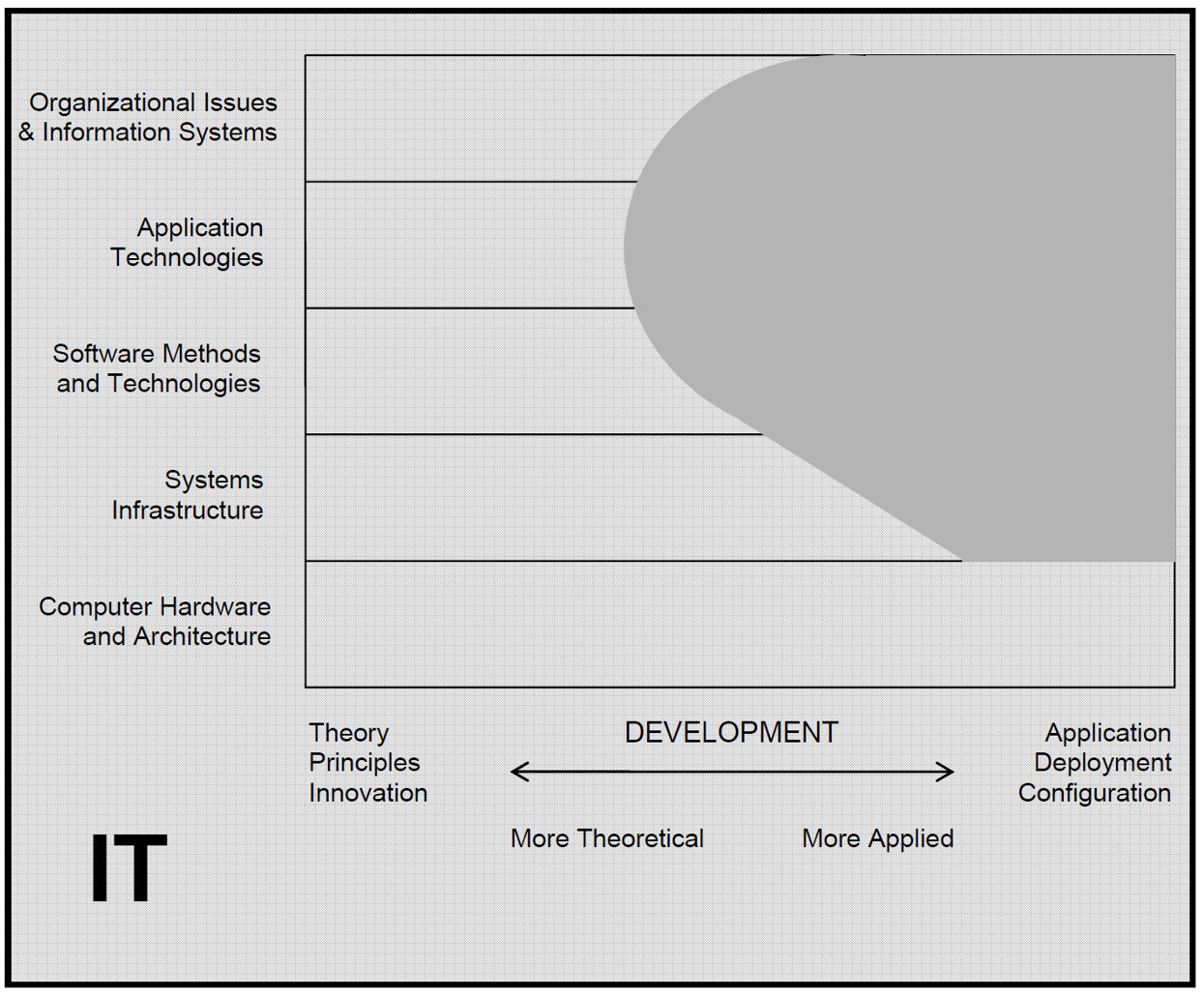
In particular, information is usually stored permanently in database. In database development (the subject of this course), critical thinking is integrated in the process. Database developers use principles of data modeling, such as the Entity-Relationship Model (ERM), to clearly and accurately understand the purposes, assumptions and the different points of views of the various types of users, to precisely specify the problem. Concepts of relational theory and data manipulation are applied to infer and construct suitable logical solutions. The implications and consequences of the design are assessed through the cost effectiveness of the database solutions.
The central question in database development is how to store and retrieve permanent data effectively for specific problems.
Fundamental and Powerful Concepts (FPC) of the Course
In ACT vocabulary, fundamental and powerful concepts form the foundation that permeates and unites a course. In this course, these concepts are:
Please see Section 2 below for more details.
1.1 Student Learning Outcomes (SLO)
After completing the course, the students are expected to be able to
For ACT assessment, SLOs #3, #4 and #5 will be used.
2. Applied Critical Thinking (ACT)
2.1 Vocabulary of Critical Thinking
We use the vocabulary of critical thinking described by Drs. Richard Paul and Linda Elder, including the eight elements of thought and nine universal intellectual standards:
Eight elements of Thought of Critical Thinking:
Nine Universal Intellectual Standards for Critical Thinking:
For more details, see:
[1] Paul, R. and Linda Elder, L., The Miniature Guide to Critical Thinking-Concepts and Tools (Thinker's Guide), 7th edition, Foundation for Critical Thinking, 2014.
[2] Paul, R. and Linda Elder, L., Critical Thinking: Tools for Taking Charge of Your Learning and Your Life, 3rd Edition, Prentice Hall, 2011.
2.2 Critical Thinking Process (CTP)
According to the ACT vocabulary we used, there are four major aspects of the Applied Critical Thinking Process, termed as the 4 C's: curiosity, connection, creativity and communication. In this course, the C in the student learning objectives is connection:
2.3 Critical Thinking Activities and Assessment
Critical thinking activities are integrated in the course. Lectures and demonstrations will include examples to highlight CT elements and intellectual standards, and their applications. This includes the uses of the CT techniques such as SEE-I, Concept Maps, and visualization tools. The instructor will highlight the relevant elements of thought in classroom examples. Homework and programming assignments contain various ACT components. Both the mid-term and final examinations include ACT-oriented questions.
In particular, data of three assessment activities (AA) on ACT will be collected to assess how well critical thinking is incorporated into the course. These assessments will be used as input to the UHCL Critical Thinking database for internal assessment of Critical Thinking, and will not directly affect your grade of the course. (However, there seems to be a positive correlation between CT assessment results and grades.)
The course assesses connections out of the four C's. The related Student Learning Outcomes (SLO) and Fundamental and Powerful Concepts (FPC):
ACT Assessment Activity |
ACT SLO |
FPC |
HW-ER |
3 |
1 |
HW-REL |
4 |
2 |
HW-SQL |
5 |
3 |
The assessment criteria for the AA:
ACT Assessment Activity |
Assessment Outcome |
||
Unacceptable |
Acceptable |
Excellent |
|
HW-ER |
[0%,80%) |
[80%,92%) |
[92%,100%] |
HW-REL |
[0%,80%) |
[80%,92%) |
[92%,100%] |
HW-SQL |
[0%,80%) |
[80%,92%) |
[92%,100%] |
Overall, if 70% or above of students are evaluated to be acceptable or excellent in each activity, as well as the average of all activities, the outcomes will be deemed acceptable. To close the loop of assessment, the instructor will evaluate the ACT content, activities, and assessment of the course, and make necessary adjustment.