Computer Systems: an introduction
CSCI 1470
by K. Yue
1. Computers
- A computer contains four major components:
- Input: devices for entering data to the computer. E.g., mouse, keyboard, drawing pad, microphone, etc.
- Processing: components for processing data. E.g., Computer Processing Unit (CPU), Graphical Processing Unit (GPU), etc.
- Storage: storage of data
- Transient data: data will be lost after programs or systesm terminate. Mainly primary memory (stored in random access memoery, RAM)
- Persistent data: data will persist after programs or systems terminate. Secondary memory such as hard disk and flash memory.
- Output: devices for presenting results, such as monitors and printers.
2. Computer Data
- Data is represented, transmitted and processed as bits.
- A bit is a binary digit, 0 or 1. It is the smallest information unit.
- A Byte is a group of 8 bits.
- A word is a fixed-sized datum handled as a unit by the instruction set of a computer processor. It is the size of primary registers of a CPU.
- Note that terms may have different meanings under different context. For example, in Microsoft's Application Program Interface (API), WORD is 2 Bytes or 16 bits.
Example:
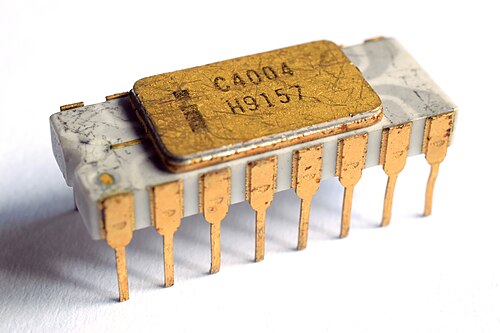
Intel 4004:
- Launched in 1971.
- Intel's first 4 bit processor.
- First microprocessor chipset
- Data Width: 4 bits
- Address Width: 12 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 740 KHz to 750 KHz
- Number of transistors: 2,300
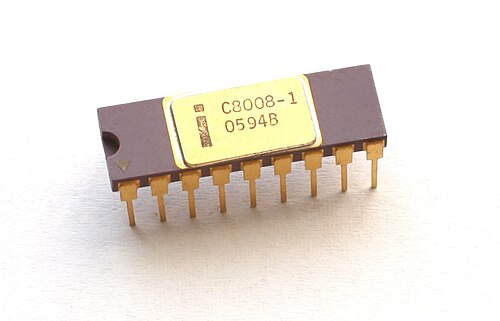
Intel 8008:
- Launched in 1972.
- Intel's first 8 bit processor.
- Data Width: 8 bits
- Address Width: 14 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 500KHz to 800 KHz
- Number of transistors: 3,500
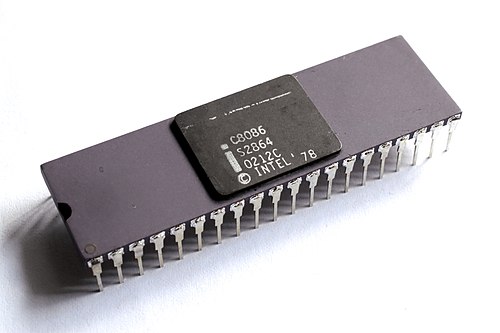
Intel 8086:
- Launched in 1978.
- Intel's first 16 bit processor.
- Launched x86 architecture.
- Data Width: 16 bits
- Address Width: 20 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 5MHz to 10 MHz
- Number of transistors: 29,000
Intel 80386:
- Launched in 1985.
- Intel's first 32 bit processor.
- Data Width: 32 bits
- Address Width: 32 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 12.5MHz to 40 MHz
- Number of transistors: 275,000
- 132 pins

Intel Pentium 4 Prescott (E0 Revision)
- Launched in 2005.
- Intel's first 64 bit processor for desktop computer (Intel 64 bit for server, Itanium, was launched in 2001),
- Data Width: 64 bits
- Address Width: 64 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 2.8 to 3.8 GHz
- Number of transistors: 125 millions
- 478 pins
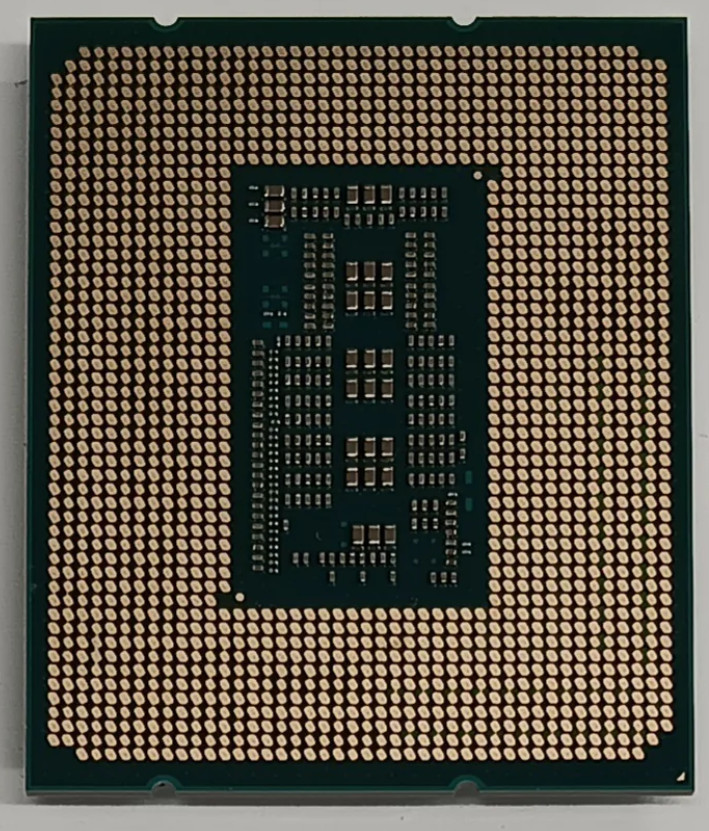
Intel Core i9-14900K
- Launched in 2023.
- $438 at Amazon, checked 8/24/2025.
- Data Width: 64 bits
- Address Width: 64 bits
- Max CPU's clock rate: 6.0 GHz
- Number of transistors: 28.5 billions
- Number of cores: 24
- Pinless design: use LGA 1700 socket to interact with the motherboard, which has 1,700 interaction with the motherboard.

3. Assembly Language
- Assembly language is a low-level programming language to instruct the CPU execution.
- Assembly language instruction has a strong, often one-to-one, correspondence with the machine code instructions that a computer's processor directly executes.
- Before a CPU can process data, data need to be hold in storage areas: registers.
- An assembly language program mainly involves more data in and out of registers and perform instructions on these registers.
- An assembly language is low level, allowing very detailed control of the computer execution. It is used mostly in systems programming and embedded systems.
- As a result, a high level language, such as Python, is used for application programming.
Example:
An assembly language program in x86 under Linux to add two numbers is shown below. You do not need to know the meaning. Note that eax, ebx, ecx, etc. are general purpose registers.
section .data
num1 dd 5 ; First number (double word - 4 bytes)
num2 dd 3 ; Second number
result dd 0 ; Variable to store the sum
section .text
global _start ; Entry point for the linker
_start:
; Load the first number into EAX register
mov eax, [num1]
; Add the second number to EAX
add eax, [num2]
; Store the result from EAX into the 'result' variable
mov [result], eax
; Exit the program (Linux specific system call)
mov eax, 1 ; System call number for sys_exit
xor ebx, ebx ; Exit code 0
int 0x80 ; Invoke kernel |
In Python:
num1 = 3
num2 = 5
result = num1 + num2 |






